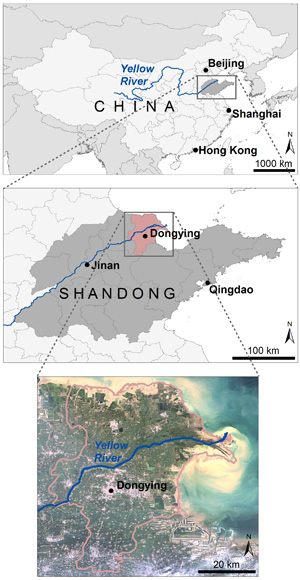
The Yellow River Delta
|
The Yellow River Delta (YRD) is located in north-east of the province Shandong, China (118°03’E - 119°20’E und 37°20’N - 38°20’N). It covers a total area of 18000 km² with a population of 5.2 million people. The whole region within the YRD is very flat with a maximum height of 17m above sea level.
Valuable economic and environmental resources
The YRD mainly consists of fertile alluvial soils that are the basis for a very valuable arable land. Moreover, the second largest oil field of China – the Shengli Oil Field – is situated in the YRD. The exploitation of Shengli Oil Field was the starting point of an intense industrialization and urbanization of the delta. The YRD is also rich in valuable minerals, rock salt, and halogens. The favourable geographic location and the resource deposits make the YRD region to one of the most important industrial centres in North-East Asia. On the other hand, the YRD represents one of the youngest wetlands on earth and it is the habitat for numerous species. The area is a particularly important resting place for millions of migrating birds of which many are under protection.
Rapid dynamics of the Delta
Due to the high sediment load of the YR the locations of the river mouth as well as the river bed have shifted several times during previous periods. In the recent delta region the YR has created almost 2500 km² of new land between 1855-1992. The newly developed cities within the delta, which grew from small settlements to a two million city (Dongying) within less than 30 years, due to the detection of the oil fields, lead to an enormous pressure on agricultural land, water resources, and natural ecosystems. Furthermore, more than 100 industrial plants located in the delta are an indirect threat to the natural habitats.
Major challenges in the Yellow River Delta region
Challenges within the delta primarily include coastal erosion and the change and shrinkage of natural wetlands. Additionally, the permanent dislocation of the main stream, the intensified intrusion of saline water, constant intervention in the nature reserves, the impacts of typhoons, and especially the increasing influence of human activities become noticeable within the natural landscape. The available amount of water within the delta for agriculture, wetlands or the regeneration of the ground water has decreased considerably, and drought phenomena and land degradation have become prevailing characteristics of the past years. Cultivable land salinizes, vegetation health – also of natural vegetation – decreases, and fragmentation of natural and cultural landscapes increases. The challenge to accomplish a balance between a high economic growth and a healthy preservation of natural resources is huge – especially since the water supply of the area is highly dependent on the developments in the upper reaches.
Key issues of the Yellow River Delta
|
Overview map of the project area. |